Active Volcanoes in Japan
Active Volcanoes in Japan
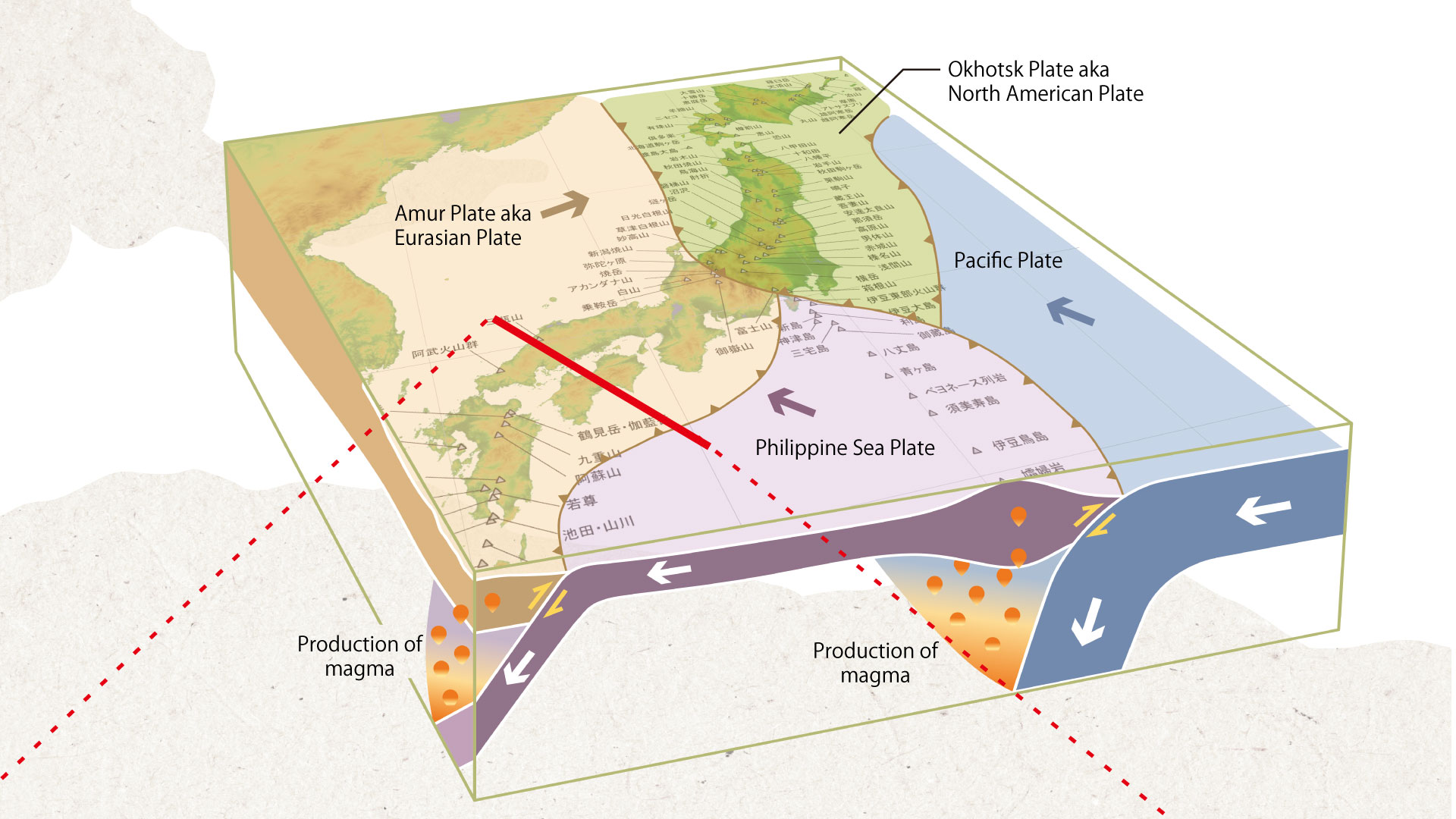
Japan is a highly volcanic country, with approximately 10% of the world’s active volcanoes.
In Japan, active volcanoes are defined as volcanoes that have erupted within the past 10,000 years, or that currently experience fumarolic activity. As of 2017, Japan had 111 active volcanoes. The number includes two in the western Honshu, Sanbe Volcano and the Abu volcanoes. The number of active volcanoes is subject to change, depending on research advances and on redefining of terms.
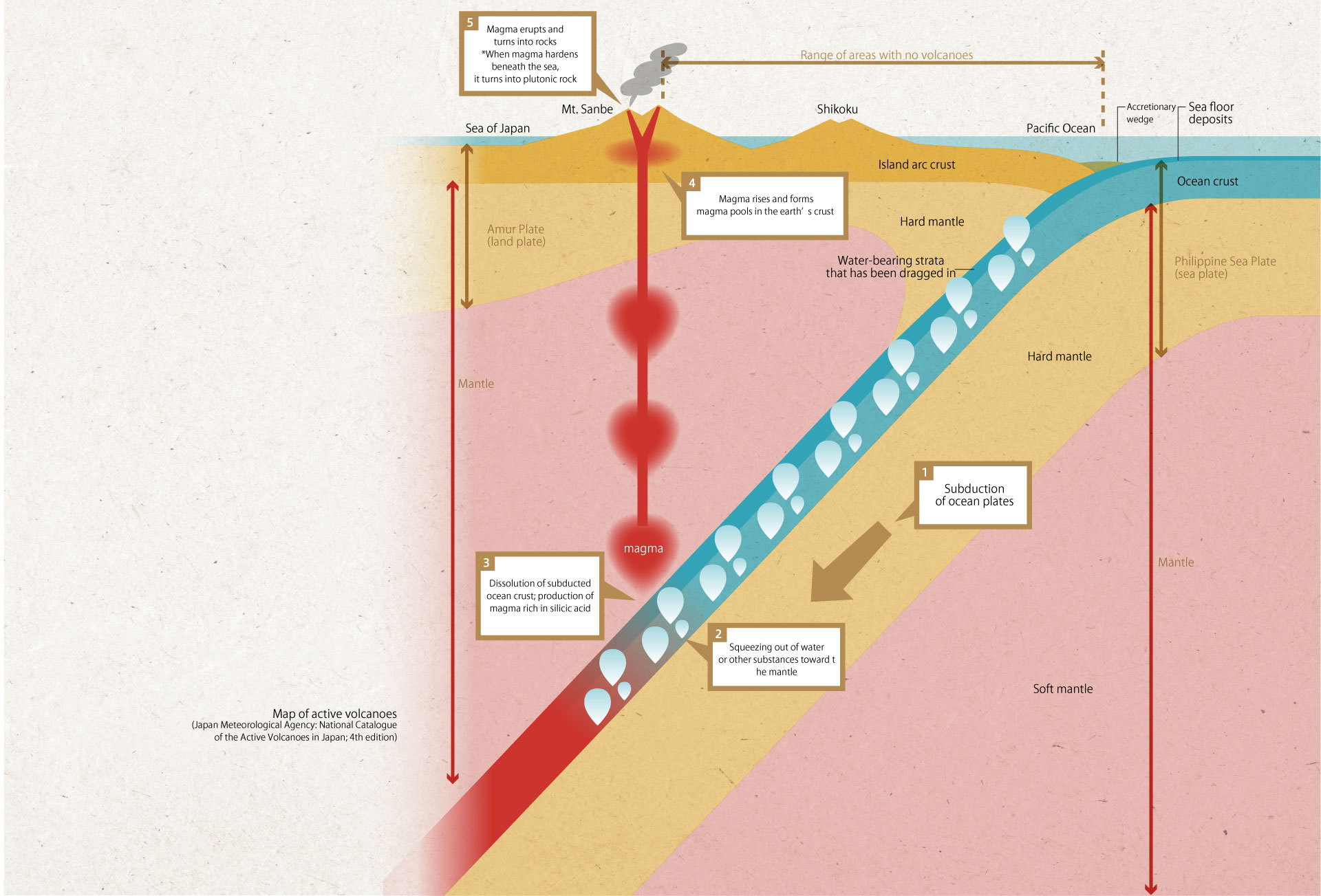
1. Subduction of ocean plates
2. Squeezing out of water or other substances toward the mantle
3. Dissolution of subducted ocean crust; production of magma rich in silicic acid
4. Magma rises and forms magma pools in the earth’s crust
5. Magma erupts and turns into rocks
*When magma hardens beneath the sea, it turns into plutonic rock
Map of active volcanoes (Japan Meteorological Agency: National Catalogue of the Active Volcanoes in Japan; 4th edition)